前一阵子在 Nu1L 队大哥们的带领下在 Defcon33 Quals 中拿到了第 4 名,小写一些游记(其实前几年也有打但是实在没有输出可写…
tiniii
附件太大,用 ida 加载了半天一直卡着,谁来给我换一个不卡的电脑…
混淆的模式大概是这样:
1
2
3
|
call loc_xxxxx
loc_xxxxxx:
add rsp, 8
|
其实就是jump一下然后忽略被压到栈上的返回地址,和 jump 基本等效,拿到手先搓了一个去混淆脚本:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
|
import idautils
import idc
import idaapi
import ida_bytes
def is_add_rsp_8(target_ea):
"""检查目标地址是否为 add rsp,8 指令"""
mnem = idc.print_insn_mnem(target_ea).lower()
op1 = idc.print_operand(target_ea, 0)
op2 = idc.print_operand(target_ea, 1)
return mnem == "add" and op1 == "rsp" and op2 == "8"
def patch_to_nop(ea):
"""将 5 字节的 call 指令替换为 5 个 nop"""
for offset in range(4):
ida_bytes.patch_byte(ea + offset, 0x90)
idaapi.create_insn(ea) # 刷新反汇编视图
def process_calls():
"""遍历所有函数中的 call 指令并处理"""
for seg_start in idautils.Segments():
seg_name = idc.get_segm_name(seg_start)
if seg_name != ".text": # 仅处理代码段(可调整或移除条件)[3,5](@ref)
continue
seg_end = idc.get_segm_end(seg_start)
ea = seg_start
while ea <= seg_end:
if idc.print_insn_mnem(ea).lower() != "call":
continue
# 获取 call 的目标地址[1,7](@ref)
target_ea = idc.get_operand_value(ea, 0)
# if not idaapi.is_mapped(target_ea): # 跳过无效地址
# continue
# 判断目标指令是否符合条件
if is_add_rsp_8(target_ea):
patch_to_nop(target_ea)
ida_bytes.patch_byte(ea, 0xE9)
idaapi.create_insn(ea)
print(f"0x{ea:x}: Call -> JMP (target: 0x{target_ea:x})")
ea = idc.next_head(ea, seg_end)
if __name__ == "__main__":
process_calls()
|
但是这个脚本跑得实在是太慢了,我就放弃调试这个脚本了…ida 启动也很慢,于是我就掏出了 pwndbg 直接开始调试。
从队友的分析结果得知(这对吗),这个二进制程序有两个固定的常量,一个长度为 800000 另一个是 1000,同时我得到了这两个数据的 dump,那么只要找到相关逻辑就行。先 rwatch 一下 Incorrect 字符串就可以大致定位到输出,然后生成几组 license 大概调试一下。不难发现程序先对 800000 的常量做了前缀和与后缀和,运算的长度和输入有关,那么产生第一个猜测程序逻辑应该是如下的:
1
2
3
4
5
|
i = int(input[0:4])
j = int(input[4:8])
pre = sum(x_80w[0:i-1])
suf = sum(x_80w[j:-1])
pre + suf == x_1k[0](sus)
|
跑了一下发现无解,后续经过一系列 fuzz 发现如果输入有 0 的话就会跳过这一组验证。只跑一个解其他全0可以过check,但是过不了hash check。
先写了脚本把所有解跑出来:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
|
x_80w = []
x_1k = []
with open('800000.dat', 'rb') as f:
while True:
chunk = f.read(8)
if not chunk:
break
if len(chunk) < 8:
chunk += b'\x00' * (8 - len(chunk))
number = int.from_bytes(chunk, byteorder='little', signed=False)
x_80w.append(number)
with open('dump_1000.bin', 'rb') as f:
while True:
chunk = f.read(8)
if not chunk:
break
if len(chunk) < 8:
chunk += b'\x00' * (8 - len(chunk))
number = int.from_bytes(chunk, byteorder='little', signed=False)
x_1k.append(number)
presum = []
s = 0
dic = dict()
for i in range(800000):
presum.append(s)
dic[s] = i
s += x_80w[i]
presum.append(s)
dic[s] = i
# print(hex(presum[0x377]))
sufsum = []
s = 0
for i in range(799999, -1, -1):
sufsum.append(s)
s += x_80w[i]
sufsum.append(s)
# print(hex(sufsum[0x378]))
for i in range(1000):
target = x_1k[i]
f = 0
for i in range(800001):
find = target - sufsum[i]
if find in dic:
f = 1
print("%.8x %.8x" % (dic[find], i))
if f == 0:
print("00000000 00000000")
print("================")
|
O(n^2) 不可接受,用 dict 反查做了个小优化。尝试先生成一组解,每组都取第二个数最小,试一下能不能过 check。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
|
def read_hex_groups(file_path):
result = [] # 最终存储所有组的列表
current_group = [] # 当前正在处理的数据组
with open(file_path, 'r') as f:
for line in f:
line = line.strip()
# 处理分隔符
if line.startswith('======='):
if current_group: # 避免空分组
result.append(current_group)
current_group = []
continue
# 处理空行
if not line:
continue
# 分割两个HEX数值
try:
hex1, hex2 = line.split()
# 转换为字节对象(每个HEX为8字节)
bytes1 = bytes.fromhex(hex1)
bytes2 = bytes.fromhex(hex2)
current_group.append((bytes1, bytes2))
except ValueError as e:
print(f"格式错误行:{line},错误:{str(e)}")
# 添加最后一组(如果存在)
if current_group:
result.append(current_group)
return result
# 使用示例
data_groups = read_hex_groups("ans.txt")
print(f"共读取到 {len(data_groups)} 组数据")
for i, group in enumerate(data_groups):
print(f"第{i+1}组包含 {len(group)} 对数据")
with open('liscense_valid.txt', 'wb') as f:
for group in data_groups:
(a, b) = group[-1]
f.write(a[::-1])
f.write(b[::-1])
|
本来还在想怎么处理多解的 hash 问题,但是这个脚本生成的解正好是正确解,直接过。
Seven-el-bee
大概是一个序列预测,猜后续 5 张牌,给了一个附件还没看,打算先上在线环境玩玩,第一次截了个图,第二次抽发现和第一次一样,秒了。
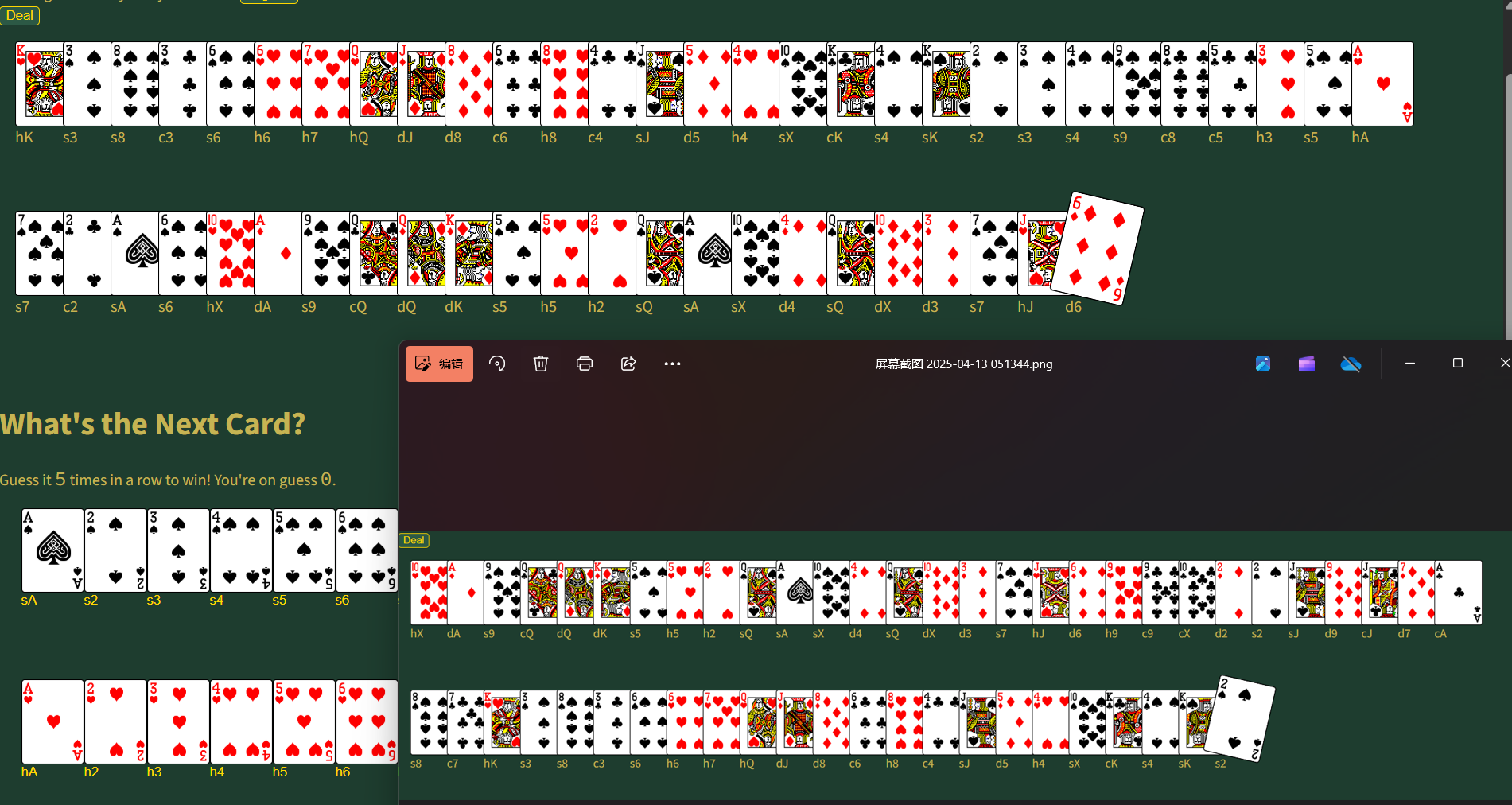
totem
按下回车发现对了,大胆猜测是逐位比较并且以输入的长度为基准,输入 f 对了,输入 a 不对,直接爆破
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
from pwn import *
import string
table = string.printable
flag = ""
for j in range(80):
for i in table:
p = process("./totem1-uploadme")
p.recvuntil(b"flag: ")
p.sendline(flag+i)
if b'Correct' in p.recv():
flag += i
print(flag)
break
p.close()
|
echoid
做梦都没有想过能在 defcon 拿到一血(
粗略逆向可以得知需要构造一个 wav 文件,经过音频指纹算法和他事先算过的一首歌高度相似。音频指纹算法有点类似 python 的 dejavu 库。
进阶逆向可以得知“高度相似”的标准是一个 score 大于 50000,先不关心这个 score 怎么来的。直接用 os.urandom 生成一个 wav 文件,发现 score 有 40000 多,那么问题就是怎么把 40000 变成 50000。先把 binary 文件 patch 成可以输出分数的。这里只需要高度相似就会输出相似分值,那么直接把高度相似的门槛改成 1,就会打出所有音频的得分。
学过算法的都知道,直接随机迭代,每次随机修改几个点,如果分数变高就留下,否则舍弃,那么得到的音频分数将会稳中向好越来越高,剩下就是时间问题。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
|
from pwn import *
import os
# p = process(["./echoid","find"])
# context.log_level = 'debug'
def makeWav(
data, # 音频数据
channel = 1, # 声道数量
sampling_rate = 44100, # 每秒采样多少次, 不能太小
BytePerSample = 1 # 每次采样多少个字节, 一般为: [1,2,3,4]
):
# 每秒多少个字节 = 声道数量 * 每秒多少次采样 * 每次采样多少个字节
BytePerSecond = channel * sampling_rate * BytePerSample
# 音频持续时间 = 字节总数 / 每秒多少个字节
# duration = len(data) / BytePerSecond
res = b'RIFF'
res+= p32(len(data)+36)
res+= b'WAVEfmt '
res+= p32(0x10) # 4字节过滤字节(一般为00000010H)
res+= p16(1) # 2字节格式种类(值为1时,表示数据为线性pcm编码)
res+= p16(channel) # 2字节通道数,单声道为1,双声道为2
res+= p32(sampling_rate) # 4字节采样率 sampling_rate, 每秒采样多少次
res+= p32(BytePerSecond) # 字节率 (4 bytes) - 每秒需要多少字节,= SampleRate * NumChannels * BitsPerSample/8
res+= p16(channel*BytePerSample) # 块对齐 (2 bytes) - 每个样本需要多少字节,= NumChannels * BitsPerSample/8
res+= p16(0x8*BytePerSample) # 比特率 (2 bytes) - 每个样本的位数,通常为8、16、24或32
res+= b'data'
res+= p32(len(data)) # 4字节 pcm音频数据大小
res+= data
return res
def find(p, data):
# data为WAV文件
p.recvuntil(b'Send us your song to be identified')
p.send(p32(len(data))+data)
def modify_data(data):
mutable_data = bytearray(data)
target_slice = mutable_data[44:-1]
slice_length = len(target_slice)
relative_indices = random.sample(range(slice_length), random.randint(0, 1000))
absolute_indices = [44 + idx for idx in relative_indices]
for idx in absolute_indices:
mutable_data[idx] = random.randint(0, 255)
return bytes(mutable_data)
from concurrent.futures import ThreadPoolExecutor
import threading
highscore = 39301 # 初始高分
lock = threading.Lock()
def run_task():
global highscore
while True:
# 获取当前高分并检查终止条件
with lock:
if highscore >= 50000:
return
current_hs = highscore
# 读取文件和处理数据(这部分不涉及共享资源)
try:
with open(f"score_{current_hs}.wav", "rb") as f:
data = f.read()
except FileNotFoundError:
continue # 文件可能已被其他线程更新
modified_data = modify_data(data) # 假设这是你的数据处理函数
# 与子进程交互(每个线程有独立进程)
p = process(["./echoid_patched", "find"])
# print("start")
find(p, modified_data) # 假设这是发送数据的函数
# print("find")
p.recvuntil("score: ")
score = int(p.recvuntil(")")[:-1])
print(score)
p.close()
# 更新高分(需要同步)
with lock:
if score > highscore:
print(f"[+] New highscore: {score} (Prev: {highscore})")
highscore = score
with open(f"score_{highscore}.wav", "wb") as f:
f.write(modified_data)
# run_task()
# 启动多线程(根据CPU核心数调整线程数)
with ThreadPoolExecutor(max_workers=10) as executor:
futures = [executor.submit(run_task) for _ in range(10)]
for future in futures:
future.result() # 等待所有线程完成
|
跑个十几分钟就能把 4w 分迭代到 5w 分通过本题。为什么只有 3 个解(
holographic
粗看是一个 mt19937 类似物,远程环境有配置的种子,先从环境变量拿到 seed1,初始化一下,然后生成一个 seed2 返回,预测生成的序列。
明显 seed2 可以 patch 过后黑盒跑一遍得到序列,因此只需要拿到远程的一组数据,然后爆破 seed1 即可。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
|
import threading
from pwn import *
found_event = threading.Event()
print_lock = threading.Lock()
def check_seed(seed):
try:
p = process('./holographic_patched', env={"SEED": str(seed)})
p.recvuntil("show me your cards \n")
p.sendline("d7 d5 cK cX sJ sQ sA h8 d9 sK s2 d3 s7 hK h9 d8 s9 s8 s3 cJ sX d6 c5 hJ h4 dQ h6 hX dX h7 cQ c9 s4 dK c4 c3 h5 hA hQ d4 c7 dA c8 s6 c6 dJ s5 c2 cA d2 h3 h2")
response = p.recv()
p.close()
return b"weren't bluffing!" in response
except:
return False
def worker(start_seed, step):
seed = start_seed
while not found_event.is_set():
if check_seed(seed):
with print_lock:
print(f"Found: {seed}")
found_event.set()
return
with print_lock:
print(seed)
seed += step
if __name__ == "__main__":
thread_count = 8
threads = []
for i in range(thread_count):
t = threading.Thread(target=worker, args=(i+0x10000, thread_count))
threads.append(t)
t.start()
for t in threads:
t.join()
|
